My Spring, 2016 political reporting class is conducting team coverage of today’s primary vote in Pennsylvania. We have compiled a short survey to learn about voters’ experience as they go to the polls today. Please take a few minutes to help us out by completing the survey here: http://goo.gl/forms/uOWk261M9I. Also, if you use Twitter, we will be live chatting about the election using the hashtag #PAprimaryTCNJ after the polls close tonight. Thanks in advance for your help and consideration, and please feel free to share this link to the survey with any Pennsylvania voters you know!
A Post-#Ferguson Reflection
This is the morning after a grand jury in Ferguson, Missouri declined to indict Officer Darren Wilson for the August 9, 2014 shooting of 18-year-old Michael Brown. I watched St. Louis County Prosecutor Robert McCulloch’s announcement, said a prayer for Brown’s family, the people of Ferguson and the protestors who filled the streets outside the police station there, as well as in cities around the country. I said a prayer for my friends in St. Louis County, some in the media, some who are educators, some in government. I said a prayer for all of the black men I know, and for all of us who love them. And then I went to bed, because I knew that the morning would come, and there would still be serious work to do.
The details of what is happening in Ferguson matter, but the response must take into account the reality that, as New Yorker writer and University of Connecticut history professor Jelani Cobb has written, “Ferguson is America.” full of fears and frustrations that, often misdirected and misplaced, circumscribe the lives of black men daily. Cobb writes:
I was once a linebacker-sized eighteen-year-old, too. What I knew then, what black people have been required to know, is that there are few things more dangerous than the perception that one is a danger. I’m embarrassed to recall that my adolescent love of words doubled as a strategy to assuage those fears; it was both a pitiable desire for acceptance and a practical necessity for survival. I know, to this day, the element of inadvertent intimidation that colors the most innocuous interactions, particularly with white people. There are protocols for this. I sometimes let slip that I’m a professor or that I’m scarcely even familiar with the rules of football, minor biographical facts that stand in for a broader, unspoken statement of reassurance: there is no danger here. And the result is civil small talk and feeble smiles and a sense of having compromised. Other times, in an elevator or crossing a darkened parking lot, when I am six feet away but the world remains between us, I remain silent and simply let whatever miasma of stereotype or fear might be there fill the void.
I was 24 years old and in graduate school. I had decided to surprise my parents by popping in for a weekend, unannounced. It must have been autumn, because it was dark when I arrived, and it was still early evening. I came in the front door and found out they weren’t home. I put my bags upstairs, turned on the kitchen light, and I saw their car pulling into the back driveway. I went downstairs to open the back door for them, reaching up with my right hand to flip a light switch, and pulling the door back with my left.. On the back lawn, I made out the figure of a young white police officer pointing his gun at me. I think he said something like, “Hands up! Police!” but I no longer remember. From the right, I heard my father’s voice, and I saw him rounding the back of the car with his arms outstretched.
“Don’t shoot! That’s my daughter!”
The officer paused. I think he turned his head to look at my father and back to me. I stood still. My father stood still, where the officer could see him. He holstered his gun. He confirmed that everything was okay and he left. The crisis had passed. Later, we learned that a neighbor had seen the light go on in the kitchen and panicked, knowing that my parents’ car was not in the driveway and I was away at school. There had been some robberies in the neighborhood. It was a simple misunderstanding, easily rectified.
Fortunately, the officer did not feel threatened. Fortunately, he was able to hear my father. Fortunately, he was not like the panicky rookie cop in Brooklyn who recently shot an unarmed man to death in a stairwell.
Of course, I was reminded of the Richard Pryor joke about one of his own encounters with the police, where he loudly intoned, “I am reaching into my wallet, to get my driver’s license,” because, he said, “I don’t to be no (bleeping) accident!” Years later, I told my Race, Gender and News students about the encounter as we discussed how one should cover the acquittal of four police officers in the shooting death of unarmed 22-year-old Amadou Diallo in the doorway of his apartment building. He was, it turned out, reaching for his identification when the heavily-armed police officers fired on him.
What if I had been male?
What if something had been in my hand?
What if my father had not shown up?
My experience was not that of Mike Brown, Amadou Diallo, or John Crawford, the 22-year-old who was shot to death (graphic video warning) in an Ohio Walmart while talking on the phone and holding a toy gun in an open-carry state. It was, however, frightening enough that I cried writing this, 33 years later. My encounter happened before the height of the crack epidemic, mass incarceration and mass marketing of the hypermasculinity and lunatic madness of corporate-sponsored gangster rap. (See Byron Hurt’s “HipHop Beyond Beats and Rhymes.”)
As the fires are doused in Ferguson, there is pain and anger in the streets. People who put their faith in peaceful protest feel betrayed. Civil libertarians worry about the militarization of police. Certainly these are important issues. TheUS Justice department may impose reforms on the Ferguson Police Department in light of this and other charges of the use of racial profiling and excessive force over a period of years.
Indeed, as former police commissioner Anthony Bouza has argued, police-community tensions reflect a larger societal failure to confront disparities of poverty and race.
Missouri Governor Jay Nixon has set up a commission to examine the root causes of and potential remedies for the region’s racial and economic divides. When Pres. Lyndon Johnson appointed a similar commission nearly 50 years ago, one of the common understandings to emerge was the need for everyone to feel as if they had a stake in the system. Author Michelle Alexander put it this way:
[T]rue justice will come only when our criminal injustice system is radically transformed: when we no longer have militarized police forces, wars on our communities, a school-to-prison pipeline, and police departments that shoot first and ask questions later. True justice will be rendered not when when a single “guilty” verdict is rendered in one man’s case, but when the system as a whole has been found guilty and we, as a nation, have committed ourselves to repairing, as best we can, the immeasurable harm that has been done.
I’ve asked friends who know the Ferguson area what young people there have to look forward to. They struggle for an answer. Jobs are scarce. Normandy, Missouri, the school system where Michael Brown earned his diploma is so poor, it lost its accreditation in 2013. In Education Week this past September, Normandy teacher Inga Schaenen argued,
Nearly every student I teach has lived through encounters with the police that nobody should ever have to experience. (I know this from their journal entries written the first week of school.) And we know from research conducted by Gloria Ladson-Billings,Alfred Tatum, and many others regarding African-American students that best practices call for teachers to actively, critically, and morally engage students’ real lives and communities. When we do so, our students will achieve academically. Pedagogically speaking, designing community-responsive, standards-based activities and lessons is a moral imperative in Normandy.
One friend to whom I posed this question directed me to St. Louis Community College’s Bridge to STEM program, which provides intensive tutoring and mentoring to prepare students with a diploma or G.E.D. for study in the life sciences. The school also offers accelerated workforce training in a range of technical fields, in partnership with local industry. Certainly, this is part of the puzzle.
But it leaves unanswered the question that Du Bois posed more than a century ago: “Training for life teaches living; but what training for the profitable living together of black men and white? Especially since, it must be acknowledged, most poor Americans are not black, and pessimism about future economic opportunities is pervasive in the US and other advanced economies.
Here, again, the work begins anew. I am a journalist and educator, not a civil rights attorney or policy maker. There is a lot to be said about how the press has covered all of this, and I will leave that to others. I want to help people find a reason for hope.
My own effort, although it may seem unrelated, is to think about how we can use media to support those who people together across lines of difference to work on common community problems. That’s part of my personal stake in projects such as SOAP, an interdisciplinary collaboration to provide New Jersey residents with accessible, comprehensive and current information about polluted properties in their neighborhoods. (If you follow the link, you won’t see much now, but there is a lot going on behind the scenes, that we hope to make public in coming months.) Our hope is that SOAP will help agencies such as Habitat for Humanity in siting affordable housing. We also hope it will be useful to Isles, a Trenton non-profit working to promote environmental and economic sustainability, in finding safe property for the dozens of community gardens its volunteers build to combat hunger. Community gardens not only help combat hunger – they may make communities safer.
This is one of several projects, and it is only a beginning. Ultimately, I think the media’s part of the solution will also have to include a shift toward what I’m calling culturally responsive journalism – a journalism that covers community responses to problems in ways that emphasize that humanity and enlarge the capacity of the community to take action to solve problems. We saw elements of that approach in the coverage of Ferguson – Michel Martin’s #Beyond Ferguson forum, for example. I still believe alternate reality games can be useful in this area. But that is another post.
-30-
Also of interest: Sheila Seuss Kennedy calls for a new GI Bill that includes a one year program of civic service and participation.
Spring semester, 2015 Research opportunities for TCNJ Journalism, Media and Public Health Students
Tip sheet: Writing stories based on data
![By Mirkolorenz (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons](http://kimpearson.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Data-driven_journalism_as_process-300x216.jpg)
Writing stories based on data: things to remember
1. It’s about the story, not the numbers. The data are just a means of illustrating a point. Make it clear why your data matters.
2. Corollary #1: find your focus and stick to it. It’s likely that during your reporting, you will come across a lot of interesting information that doesn’t fit your story. Lose it. As Faulkner is reported to have said, in writing, “you must kill all of your darlings.”
3. When comparing statistics, make sure the comparisons are valid. This is a problem that often occurs when looking at data over time. For example, some years, the government changed the way it counted unemployment statistics. A longitudinal comparison of unemployment rates would need to take that into account. Another example that we discussed in class concerned the way various states defined “sex crimes” for reporting purposes under Megan’s Law. SAT scores are another well-known example.
4. Corollary to #3: if you are comparing two sets of similar data, make note of differences in sampling methods, error margins or other differences that might reduce the validity of the comparison.
5. Place examples in context – but make sure it’s the right context. For example, let’s say I report that Osama bin Laden’s family has given millions of dollars to Harvard University. (This is true.) I would convey the wrong impression if I didn’t also point out that Osama bin Laden was estranged from his family, which denounced his terrorist activities. In addition, Osama’s brother is a Harvard graduate, which explains part of the relationship between the family and the university.
6. Make sure your data and analyses come from authoritative sources. If an individual who works for an organization makes an assertion about an organization’s history or policies, get written documentation or verification where possible. The employee might be repeating something he or she has heard, and it may or may not be accurate.
7. Corollary: The same thing is true for people who work in highly-specialized fields such as health care or law. When I worked in oncology, one of my jobs was to edit a publication that would provide allied health professionals with accurate, research-based information about cancer, because we were constantly getting calls from people who called us about information they had been given by a nurse or other medical professional that turned out to be inaccurate.
Particulate Matter: What is it and what does it do
Particulate Matter (PM) is a mix of solid and liquid pollutants that can be separated into the two categories depending on their size. PM2.5 are fine particles that are 2.5 micrometers in diameter; PM10 are coarse particles that are between 2.5 and 10 micrometers. Additionally, there is a category known as ultrafine particles, which are smaller than 0.1 micrometers.
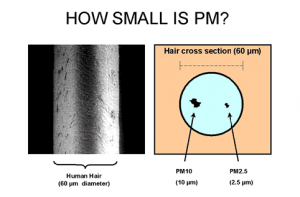
PM can originate from various sources, which then determine the composition of the PM and the effects it could cause. Typically, PM is made up of nitric acids, sulfuric acids, other organic chemicals, metals, and soil/dust particles. PM10 primarily are dust and soot, which can be from vehicles on roadways and industrial areas. PM2.5 are generally from forest fire smoke and industrial combustion sources.
PM can be in the form of smoke, soot, dust, salt, acids, and metals. Additionally, PM can be from gaseous nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides when they are released into the atmosphere (typically from burning fossil fuels) and undergo chemical reactions with the ozone to become PM. This reaction is called oxidation. Further reaction with water vapor can lead to acid rain formation.
Because they are so small, PM can be easily breathed in by people, entering the respiratory system and wreak havoc on their cardiovascular system. PM10 is large enough to get caught in mucus or cilia of the nose and throat, which will lead to coughing and expelling the particulate matter out.
PM2.5 are small enough to enter the lungs, as deep as the bronchioles (passageway from nose or mouth to the air sacs) and alveoli (air sac surrounded by artery and veins, which is where the blood cells exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen). Because PM2.5 can penetrate deeper into the lungs, the severity of the health effects increases.
Ultrafine PM can integrate into the bloodstream through the alveoli. This causes PM to spread throughout the body into organs such as the heart and brain. PM is made up of toxic pollutants. Accumulation of PM in the body can create chronic respiratory problems. For people with heart or lung diseases and exposure to PM have a higher risk of premature death and heart attacks. Overall any prolong exposure to any PM is toxic and leads to health problems. When exposed to PM, people with existing heart and lung diseases, young children, and the elderly are at high risk for health complications.
Since 1995, the National Center of Environmental Research (NCER) has been studying PM to further understand its health impacts on people and the environment. Their discoveries will help set up the PM National Ambient Air Quality Standards. Research will allow both the government and public to understand what PM is and what to do about it.
Information obtained from Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Clean Heat Asbruton
- «Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- 14
- Next Page»